Abstract
The digitalWrite() sets the specified digital pin to HIGH or LOW. To make the pin HIGH it sets the value of the corresponding bit of the register to 1, or to make the pin LOW, it sets the bit to 0.
There are three registers, PORTB, PORTC and PORTD. The relation of the registers and the pins of Arduino Uno is shown below. Ax is an analog pin, Dx is a digital pin.
| PORTB | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bit | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| Pin | - | - | D13 | D12 | D11 | D10 | D9 | D8 |
| PORTC | ||||||||
| Bit | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| Pin | - | - | A5 | A4 | A3 | A2 | A1 | A0 |
| PORTD | ||||||||
| Bit | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| Pin | D7 | D6 | D5 | D4 | D3 | D2 | D1 | D0 |
The rough diagram to convert Arduino pin number to ATmega328P register is shown below.
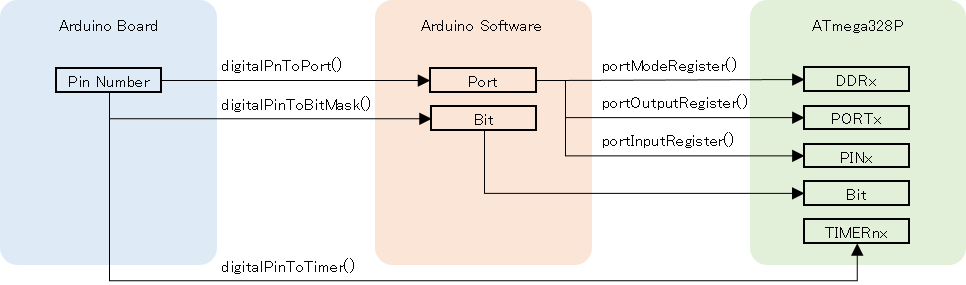
The digitalRead() is a function that dose
- calculate which bit of PORTx to for the pin
- make the bit 1 to output HIGH or 0 to output LOW
Source Code
The digitalWrite() is defined in hardware/arduino/avr/cores/arduino/wiring_digital.c as below.
|
|
The input arguments are pin and val. The type of the arguments are uint8_t.
First calculate the timer of the pin. Some of the digital pins are related to timer. These pins can output PWM.
|
|
The digitalPinToTimer() is a macro defined in hardware/arduino/avr/cores/arduino/Arduino.h. It returns a timer name if the pin is related to a timer. If not, it returns NOT_ON_TIMER.
Next calculate the bit mask, which bit in the PORTx, of the pin.
|
|
The digitalPinToBitMask() is a macro defined in hardware/arduino/cores/arduino/Arduino.h. It returns a value with a corresponding bit, shown in the table above, of DDR set to 1. For example, if the pin is 13, the value 0b00100000 is returned. It means the fifth bit of PORTB.
Next, calculate a port corresponds to the pin.
|
|
The digitalPinToPort() is also a macro defined in hardware/arduino/cores/arduino/Arduino.h. It returns the PORT corresponds to the pin. If the pin is from 0 to 7, it returns PD, from 8 to 13 it returns PB, from 14(A0) to 19(A5) it returns PC.
If the port is NOT_A_PIN, the function returns immediately.
|
|
In case of Arduino Uno, if the input value is correct/valid, digitalPinToPort() dose not return NOT_A_PIN. If the input value is incorrect/invalid, it refers to the out of range of an array, and its behavior is undefined. This means we must not give an incorrect input parameters.
If the pin is related to a timer, PWM output is stopped.
|
|
The turnOffPWM() is a function defined in hardware/arduino/cores/arduino/wiring_digital.c, and it stops the timer.
|
|
The portOutputRegister() is a macro defined in hardware/arduino/cores/arduino/Arduino.h. It converts the port to an address. It returns one of the PORTB, PORTC or PORTD. If the port is equal to PB, it returns PORTB.
At the end, if the input argument val is LOW, sets the bit of the port to 0, if not sets the bit of the port to 1.
|
|
The SREG is a status register which holds interrupt enable flag, carry flag and so on. Before changing the pin mode, SREG is stored to oldSREG. Then disable an interrupt using cli().
To make the specified bit of a variable 0, invert the bit and calculate a logical AND. For example, if the pin is 13, the bit is 0b00100000, so ~bit is 0b11011111. Calculating this logical AND with this value and DDR, the bit which corresponds to the pin 13 would be 0.
To make the specified bit of a variable 1, calculate the logical(bitwise) OR.
Then it puts the oldREG back to REG.
Version
Arduino AVR Boards 1.8.6
Last Update
March 21, 2023